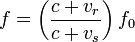Chapter 5: Waves and Interference
by Saree Costa, Mario Jaramillo and Christina Kogat
Periodic Motion
Periodic Motion: A predictable motion that is regular and repeating. Periodic Motion
can best be seen in simple examples that we see daily. The two easiest examples to show periodic
motions are a bouncing ball and a pendulum.
- Bouncing Ball: When you bounce a ball, a rubber ball, it will bounce for a long time.
Thanks to internal friction and the resistance air provides the rubber ball will come to a stop
eventually. A rubber ball that is perfect would bounce forever if there
were no resistance (friction).
- Pendulum: When a weight on a string is swung, it
will go back and forth in a periodic motion. Once the force is applied to the pendulum and
it is swinging, would keep going back and forth forever if there were no resistance.
frequency (f): the number of crests passing a certain point in a unit of time
Period (T): the ime for one wave to pass a given point (measured in seconds)
T=1/f
Waves
Wavelength (λ): the length of a repeating wave shape
speed (v):
Amplitude (A): the maximum displacement of particles of a medium
v=fλ
Energy → A2
Sound Waves
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect was originally discovered by Austrian mathematician and physicist
Christian Doppler (1803-1853) and is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving
relative to the source of the wave. For example, when a police is car coming towards
you then passing you, the pitch of the siren becomes higher then lower. The change in
pitch is due to a shift in the frequency of sound waves. The closer the siren gets to the
observer, the more the sound waves become compressed with the intervals between
the waves diminishing, increasing the pitch. When the source of the waves (the siren in this case)
move towards the observer, each successive wave is emitted closer to the observer than the
last, thus taking less time. As the siren moves further away, the
sound waves are stretched causing the pitch to decrease. By measuring the rate of change of
pitch, we are able to determine speed. The relationship between observed
frequency f and emitted frequency f0 is given by:
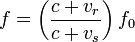
Where: is the velocity of waves in the medium is the velocity of the receiver
relative to the medium; positive if the receiver is moving towards the source. is the
velocity of the source relative to the medium; positive if the source is moving away from
the receiver.
Electromagnetic radiation emitted by a moving object also exhibits the Doppler effect.
The radiation moving towards an observer is compressed, increasing the frequency (blueshift).
In contrast, when the object is moving away, the radiation is stretched (redshift).
Stars, galaxies and gas clouds exhibit blueshifts and redshifts.

In astronomy, the Doppler effect applies to electromagnetic waves in all portions of
the electromagnetic spectrum, not only the visible part. Astronomers are bale to use the
Doppler effect to measure how fast celestial bodies move toward or away from the
Earth.
Mechanical Waves:
A mechanical wave is a wave that requires a medium with which to travel (solid, gas, liquid, plasma),
as well as an input of initial energy (a disturbance/vibration in matter). There are three types of
mechanical waves, including:
- Transverse Waves
- Longitudinal waves
- Surface waves
Some examples of mechanical waves:
- Ocean waves: formed by vibrations in a liquid
- Sound waves: formed by vibrations in a
gas (air)
- Waves on a rope
Electromagnetic Waves:
In contrast with mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves do not require any medium to
travel. Electomagnetic waves can, however, still travel through a medium. In addition to having
the ability to travel through solid, gas, liquid, and plasma, electomagnetic
waves can also travel through the vacuum of space.
Interference
Superposition Principle: If there are more than one source of waves, the net amplitude at a
particular location equals the sum of the amplitudes of the waves from each of the sources.
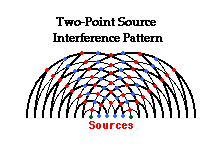
Two Source Interference:
Waves produce two-point source interference patterns when the two sources periodically disturb
the medium at the same frequency. The pattern can be characterized by a pattern of
alternating nodal and antinodal line. The proximity of anti--nodal lines is contingent
on the waves' wavelength.
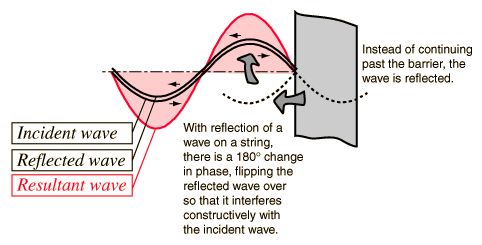
Standing Waves:
A standing wave is a vibrational pattern created in a medium when the vibrational frequency
of the source causes reflected waves from one end of the medium, such as a string, to interfere
with the incident waves from the source. This interaction creates
specific points on the medium to appear as if standing still thus the name. However a
standing wave pattern only occurs at specific frequencies of vibration known as harmonics.
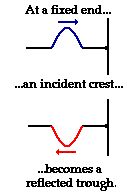
For example, if an upward pulse is introduced at the left end of a slinky, the pulse will travel
rightward across the slinky until it reaches the fixed end on the right side of the slinky then will
reflect and inverse. Now the upward pulse is a downward
pulse. If another upward pulse is introduced at the exact moment when the first pulse is reflected,
the two pulses will meet in the middle of the slinky and undergo destructive interference, the point
of no displacement. The points at which there is almost
no disturbance are the nodes while the areas where there is a large disturbance are the antinodes.
- y0 is the amplitude of the wave
- ? (called angular frequency,
measured in radians per second) is 2p times the frequency (in hertz)
- k (called the wave number and measured in radians per meter)
is 2p divided by the wavelength ? (in meters), and
- x and t are variables for longitudinal position and time, respectively.